Using STorM32 with ArduPilot: Difference between revisions
| Line 198: | Line 198: | ||
With BetaPilot installed, the flight controller supports the STorM32's Gimbal Protocol V2. It can be enabled/configured via the MNT_ZFLAGS bitmask parameter. | With BetaPilot installed, the flight controller supports the STorM32's Gimbal Protocol V2. It can be enabled/configured via the MNT_ZFLAGS bitmask parameter. | ||
For more info see [MAVLink_Communication#Gimbal_Protocol_V2]. | For more info see [[MAVLink_Communication#Gimbal_Protocol_V2]]. | ||
== Testing the Connection == | == Testing the Connection == | ||
Revision as of 09:57, 26 November 2020
The information on this page refers to firmware v2.52 and BetaPilot 4.0 v0.48, and higher.
The STorM32 gimbal controller can communicate with an ArduPilot flight controller via a serial UART data line. The serial communication allows for a much richer data transmission and accordingly richer set of features than possible with the traditional PWM connections. Examples are advanced control functions, the STorM32-Link or the NT Camera features. It also can lead to a much cleaner wiring.
If you just need the range of functionality possible with the standard tilt & pan control, then you don't need anything of the following, and you may stop reading. Some of the more basic features discussed below can also be accomplished by workarounds. Decide yourself which approach fits your needs best. :)
STorM32 - ArduPilot Support
ArduPilot offers two mount types, which can be used with the STorM32 controller, the SToRM32 MAVLink (MNT_TYPE = 4) and SToRM32 Serial (MNT_TYPE = 5) mounts. For further details please visit ArduPilot Docs > Copter > Optional Hardware > Camera&Gimbals > SToRM32 Gimbal Controller.
Comment: Unfortunately, ArduPilot's gimbal support is partially flawed. That is, many features you will find to work great, but some you will find to not work well. STorM32 can't do anything about it, it's ArduPilot. Please also note that the STorM32 firmware author is not responsible for the implementation of ArduPilot's mount types.
The BetaPilot fork of ArduPilot additionally offers the STorM32 MAVLink2 (MNT_TYPE = 83) mount type, which provides the best range of functions.
A comparison of the different techniques to connect the STorM32 controller with the flight controller is given in the following feature matrix:
Feature Matrix
(to the best of the authors knowledge)
| Feature | PWM | SToRM32 MAVLink | SToRM32 Serial | BetaPilot / STorM32 MAVLink2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gimbal Angle Control | x | x (?) | x | x |
| MOUNT_STATUS message | - | x (1) | x (2) | x |
| ATTITUDE message | - | - | - | x |
| Camera Trigger | x | x | - | x |
| Gimbal Point in MP | - | x | x (2) | x |
| Solo Smart Shots | x (3) | - | - | x (3) |
| Camera Manager in QGC | - | x (4) | - | x |
| MAVLink Parameters | - | x | - | x |
| Video Control in Missions | - | x | - | x |
| 360° Gimbal with Free Look | - | - | - | x |
| STorM32 Functions | - | - | - | x |
| STorM32 Scripts | - | - | - | x |
| STorM32-Link: Horizon Drift Comp. | - | - | - | x |
| STorM32-Link: Yaw Drift Comp. | - | - | - | x |
| MAVLink Passthrough Configuration | - | - | - | x |
| MAVLink Camera Micro Service | - | - | - | x |
| MAVLink Advanced Features | - | - | - | x |
| MAVLink Statustext messages | - | - | - | x |
| STorM32 Gimbal Protocol v2 | - | - | - | x |
| Prearm Checks | - | - | - | x |
(?) Many but not all features work in the latest ArduPilot releases. Please check with the ArduPilot community.
(1) The message reports the last set point, not the actual gimbal/camera orientation.
(2) Works only for deprecated v0.9x firmwares.
(3) Only up to ArduCopter 3.6. ArduCopter 4.0 has introduced two bugs which the STorM32 controller cannot work around.
(4) Only basic features.
Comment: Note that some of the listed features only need BetaPilot but do not require that also the STorM32 MAVLink2 mount (MNT_TYPE 83) is enabled; this is so since they are standard MAVLink.
BetaPilot
BetaPilot, which includes BetaCopter and BetaPlane, is a fork of ArduPilot, with modifications which are largely directed at the STorM32 gimbal controller. If you want to make best use of your STorM32 gimbal and want 2020-ish capabilities, then you definitely want to chose BetaPilot (BetaCopter/BetaPlane). :)
In order to establish a working communication between the STorM32 controller and the flight controller, parameters in both the flight controller and the STorM32 controller need to be adjusted, as described in the following.
The BetaPilot fork implements the latest MAVLink standard as well as the STorM32 MAVLink2 mount type (MNT_TYPE = 83), which make the following features possible.
Comment: Before using BetaPilot (BetaCopter/BetaPlane) it is strongly recommended to first install the original ArduPilot firmware and get the vehicle operating flawlessly with it, and only then to install BetaPilot.
STorM32 MAVLink2
The STorM32 controller needs to be connected via one of its UART ports to one of the UART ports on the flight controller, and these settings be made:
Settings in STorM32:
- Mavlink Gimbal = “Gimbal1” or higher
- Mavlink Gimbal Stream = “attitude status” or higher
- Mavlink Uart Port = “uart” if the UART port is used (this is the default)
The other settings can normally be left at their default. The STorM32 controller needs to be rebooted when you change the UART port. A complete description of the configuration parameters is provided in the article MAVLink Communication.
Settings in BetaPilot:
- MNT_TYPE = 83
- SERIALx_PROTOCOL = 2
- SERIALx_BAUD = 115
SERIALx can be any of the available serial ports SERIAL1, SERIAL2, and so on. This enables the STorM32 MAVLink2 mount. The flight controller must be rebooted for the changes to become effective.
With these settings you should notice:
- In MissonPlanner or any other GCS, a additional MAVLink component named GIMBAL will be present.
- In the STorM32 [GUI:Dashboard], the MAVLINK field will show PRESENT.
- In the STorM32[GUI:Dashboard], the STorM32-Link field will show PRESENT or a similarly positive message.
This provides some quick indicators for whether things are working or not.
The above settings provide a basic configurations. Some features need additional parameters to be adjusted.
Comment: The default baudrate for the STorM32 serial ports is 115200 bps, hence in ArduPilot SERIALx_BAUD has to be set to 115. However, other baudrates can be configured; e.g., for 230400 bps one sets the STorM32 parameter Uart Baudrate to “230400” and the ArduPilot parameter SERIALx_BAUD to 230.
STorM32 via UAVCAN
The STorM32 controller can also be connected via CAN bus to the ArduPilot flight controller (see UAVCAN).
STorM32-Link
Requires this additional setting:
Settings in STorM32:
- STorM32Link Configuration = “v1”
With MNT_TYPE = 83, the flight controller also sends out the STorM32-Link data to the STorM32 gimbal, but these data are used by the STorM32 controller only when STorM32Link Configuration = “v1” is also set.
Comment: This setting does not affect the message shown in the [GUI:Dashboard] STorM32-Link field! The message shown there, such as 'not available', PRESENT, INUSE, OK, reflects the incoming data stream, not its usage.
For more details on the STorM32-Link, please read the article STorM32-Link.
Virtual Channel Configuration
Requires this additional setting:
Settings in STorM32:
- Virtual Channel Configuration = “serial”
With this setting, all STorM32 functions can be invoked by selecting any of the “Virtual-1” - “Virtual-16” input channels, exactly as one would do it if the STorM32 controller would be directly connected to a receiver using the traditional means (PWM, PPM, sbus, and so on).
This allows us to do many useful things, such as activating a script or triggering video on/off from the transmitter. It however also allows us to do nonsense, and it is in the user's responsibility to avoid that. For instance, if ArduPilot is in Rc Targeting mode, and e.g. Rc Pitch Control is set to a virtual input channel, then the gimbal may move in funny ways since it may receive the transmitter stick information from both ArduPilot and the receiver. On the other hand, if ArduPilot is in GPS or ROI Targeting mode, then one gets "free look", which is useful and quite cool actually. As said, all this is exactly as if the receiver would be directly connected to the STorM32 controller on its RC ports.
Passthrough Configuration
This feature allows you to connect the STorM32 GUI to the USB or any (MAVLink enabled) serial port of the flight controller, and to directly communicate with the STorM32 gimbal.
This is extremely convenient for configuring STorM32 gimbals when they are e.g. installed permanently in the vehicle. This also works via a wireless telemetry link, and thus opens the option of e.g. tuning the gimbal during flight, and further unheard of possibilities for controlling the gimbal during flight.
This preliminary demo video demonstrates the pass-through feature:
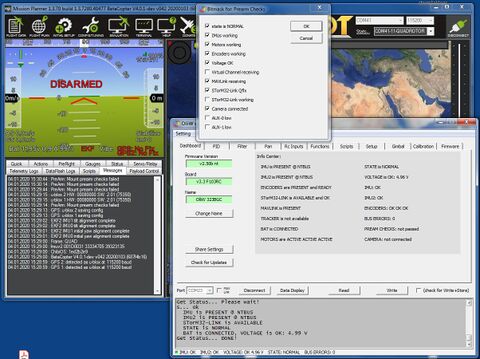
Prearm Checks
Requires this additional setting:
Settings in STorM32:
- Prearm Check != “off”
Settings in BetaPilot:
- MNT_ZFLAGS = 128 (this is a bitmask, so 128 means that the 8-th bit should be set by adding 128 to the value)
The STorM32 controller supports a rich set of prearm checks. The status of the prearm check is passed on to the flight controller, and lets it handle it exactly like any of its other prearm checks. For instance, in a GCS it will display a message "PreArm: Mount prearm checks failed" in intervals of 30 seconds.
This provides a simple and quick check that the STorM32 gimbal is working as intended.
Statustext Messages
With BetaPilot installed, the flight controller sends various MAVLink STATUSTEXT messages to a ground control station, providing additional information.
In addition, MAVLink STATUSTEXT messages can also be send via STorM32 scripts, the SENDMAVTEXT command specifically. This provides a very versatile mechanism to communicate to the user.
STorM32 Gimbal Protocol V2
With BetaPilot installed, the flight controller supports the STorM32's Gimbal Protocol V2. It can be enabled/configured via the MNT_ZFLAGS bitmask parameter.
For more info see MAVLink_Communication#Gimbal_Protocol_V2.
Testing the Connection
The serial MAVLink connection can be tested in several ways. The following tests do not require that the vehicle is completely built and/or set up, and do not require that the vehicle is armed.
- MAVLINK field in the STorM32 GUI: The [GUI:Dashboard] has a field named MAVLINK. It should display PRESENT.
- STorM32-LINK field in the STorM32 GUI: The [GUI:Dashboard] and [GUI:Data Display] each have a field which is related to the STorM32-Link. They should display PRESENT, AVAILABLE or OK.
- MissonPlanner or QGroundControl: An additional MAVLink component named GIMBAL should be present.
- Message box in MissonPlanner: With the GIMBAL component selected, in the message box several text messages related to the STorM32 gimbal should appear. In particular, a message like "STorM32 v2.40 nt v1.30 F103RC" informing about the STorM32 firmware version should be visible.
- Gimbal RC Targeting: With ArduPilot in RC Targeting mode (which should be the default mode), the gimbal can be moved with the transmitter sticks.
Gimbal Point
MissionPlanner supports what it calls a 'gimbal point'. It is a blue point icon on the map, which indicates the estimated position at which the gimbal is looking at (see also e.g. https://github.com/ArduPilot/MissionPlanner/issues/1323). In order to activate it, the following ArduPilot parameters must be set:
Settings in ArduPilot:
- MNT_STAB_ROLL = 0
- MNT_STAB_TILT = 1