What is STorM32 NT about?: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
One of the major drawbacks of the "old" STorM32 is the reliance on the I2C bus for communicating with the IMU(s), because of I2C | One of the major drawbacks of the "old" STorM32 is the reliance on the I2C bus for communicating with the IMU(s), because of the sensitivity of I2C to disturbances from e.g. the motor signal wires (see the [[I2C Error Compendium]]). The STorM32 NT provides an ultimate solution by replacing the I2C bus with the NT bus, which hardware-wise is nothing else than just a standard serial TTL UART, but at a quite high baudrate. Since the UART is low resistance and push-pull the disturbance sensitivity is very much lower than for I2C, making it practically error free. Furthermore, even if a transmission error should occur, the controller has no difficulties to recover from it, unlike with I2C. | ||
The additional cool thing about the NT concept is that it does not stop here. As with any bus also the NT bus allows one to not only connect one IMU module but also further modules, such as a 2nd NT IMU module, motor driver modules, a camera controller module, a data logging module, and so on. This provides us with a number of further advantages: | The additional cool thing about the NT concept is that it does not stop here. As with any bus also the NT bus allows one to not only connect one IMU module but also further modules, such as a 2nd NT IMU module, motor driver modules, a camera controller module, a data logging module, and so on. This provides us with a number of further advantages: | ||
Revision as of 05:59, 24 June 2019
One of the major drawbacks of the "old" STorM32 is the reliance on the I2C bus for communicating with the IMU(s), because of the sensitivity of I2C to disturbances from e.g. the motor signal wires (see the I2C Error Compendium). The STorM32 NT provides an ultimate solution by replacing the I2C bus with the NT bus, which hardware-wise is nothing else than just a standard serial TTL UART, but at a quite high baudrate. Since the UART is low resistance and push-pull the disturbance sensitivity is very much lower than for I2C, making it practically error free. Furthermore, even if a transmission error should occur, the controller has no difficulties to recover from it, unlike with I2C.
The additional cool thing about the NT concept is that it does not stop here. As with any bus also the NT bus allows one to not only connect one IMU module but also further modules, such as a 2nd NT IMU module, motor driver modules, a camera controller module, a data logging module, and so on. This provides us with a number of further advantages:
- The NT modules can be daisy-chained, which can result in quite clean wiring, and helps tremendously with e.g. slip rings.
- The NT modules can be replaced easily, resulting in extraordinary flexibility in the configuration. For instance, if one needs higher motor power, one just needs to install a NT motor module with higher amperage.
- The possibility to replace individual NT modules may reduce costs in case of damage.
- The concept simplifies integration of technological advances: If you need encoders, build and code a FOC motor driver module (see T-STorM32), if you need a high-quality ultra-low drift IMU module, build and code a high-quality ultra-low drift IMU module, if you need a CHDK camera controller, build and code a CHDK camera controller, and so on.
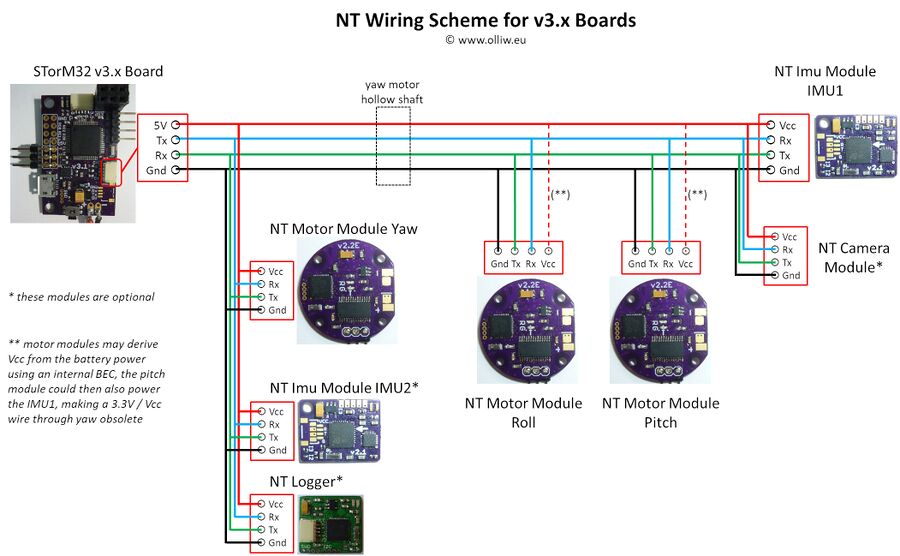
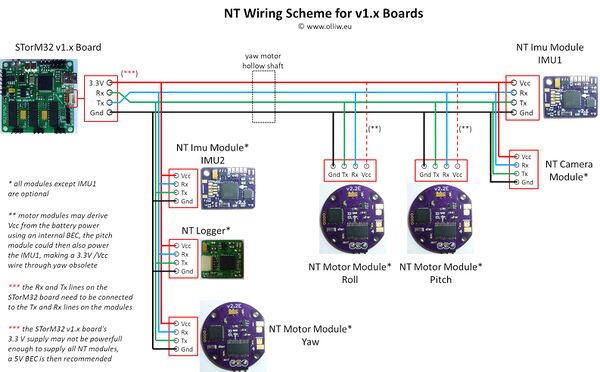
The schemes below show, for the v3.x and v1.x controller boards, what could be a typical, fully NT-ized configuration.
One further cool thing about the NT concept is that one can continue to use the widely and cheaply available v1.x STorM32 boards. The NT concept is fully compatible with them! Technically this is possible because the microcontroller pins used for the I2C port can also be configured as UART pins, turning them into the NT bus. Even though one doesn't need a new controller board, one nevertheless needs new hardware, at minimum one NT IMU module.
However, it is pointed out that all one needs to start with is only one NT IMU module to replace the "old" I2C camera IMU. All other modules are optional, and not using them doesn't incur any restrictions in functionality. For them a simple rule applies: Whenever a NT module is found it is used, and when not the conventional hardware is used. For instance, if a 2nd NT IMU module is not on the NT bus, then the on-board IMU or a I2C-based IMU connected to the I2C#2 port is used. Similarly you can continue to use the STorM32's motor driver outputs M0, M1, and M2, or the IR led, and so on.
The wiring scheme is slightly different for a v1.x STorM32 controller board (note the "crossing" of the Tx/Rx lines at the NT connector on the STorM32 board):