Using a ESP8266 Wifi Module: Difference between revisions
(→GUI) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
<!-- | |||
== Brief == | == Brief == | ||
| Line 90: | Line 91: | ||
By default the ESP is configured as access point with ssid "STorM32 ESP" and password "thisisgreat". So, connect to it, start the browser, and go to 192.168.4.1. Alternative, start the GUI and choose "ESP" in teh Port field. | By default the ESP is configured as access point with ssid "STorM32 ESP" and password "thisisgreat". So, connect to it, start the browser, and go to 192.168.4.1. Alternative, start the GUI and choose "ESP" in teh Port field. | ||
You are greatly encouraged to improve the javascript and css files. This is made very easy. The ESP just provides a very rudimentary HTML skeleton, everything essential is filled in by the js and css scripst, and these are stored in the ESP's filesystem. In order to use your own js and css, you just have to upload them to the EPS's filesystem (step 3). You also can provide links to js and css files on your own webspace, which makes development most easy. See storm32web.cfg for details. | You are greatly encouraged to improve the javascript and css files. This is made very easy. The ESP just provides a very rudimentary HTML skeleton, everything essential is filled in by the js and css scripst, and these are stored in the ESP's filesystem. In order to use your own js and css, you just have to upload them to the EPS's filesystem (step 3). You also can provide links to js and css files on your own webspace, which makes development most easy. See storm32web.cfg for details. | ||
Revision as of 02:47, 20 July 2017
The information on this page refers to firmware v2.29e and higher.
Since firmware version v2.28e, communication via Wifi using the popular ESP8266 Wifi module is supported.
Ordering Information
Things to have at minimum:
- ESP8266 Wifi Module with 1MB (8Mb) flash
- USB-to-serial adapter (or a v3.x STorM32 board)
The ESP8266 Wifi module in the list is obvious. If you are using a v1.x STorM32 board, when you need in addition a USB-to-serial adapter. It is required for flashing the ESP8266 module with a dedicated firmware and upload other files to the ESP8266. However, you probably have one anyhow. For STorM32 v3.x boards this is not needed.
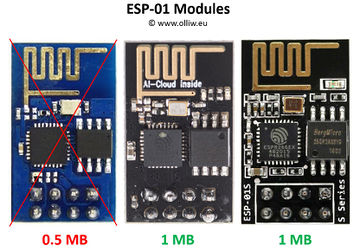
It is important to get the correct ESP8266 module. Quite many different versions are available, see e.g. [1]. You need a module with 1 MB (8 Mb) flash, since the STorM32's ESP firmware is made for that flash size.
In principle, any ESP8266 module with said flash size can be used. The STorM32 v3.x boards are however prepared for hosting a ESP-01 module. The original ESP-01 module has only 512 KB (4 Mb) flash and is thus not suitable. You need a "new" ESP-01 module, which nowadays are in fact mostly sold. These are typically black instead of blue, and come with a label "AI-Cloud inside", or as ESP-01s "s series". However, as always with this Asian stuff, one can't be absolutely sure, so buy with care.
Installation
The installation consists of four steps: flashing the ESP8266 module with the dedicated firmware, uploading some data files to the ESP8266 module, connecting the ESP8266 module to the STorM32 controller, and configuring the STorM32 controller.
Flashing the ESP8266
Uploading of Data Files to the ESP8266
Connecting the ESP8266 to the STorM32
STorM32 Configuration
ESP8266 Operation Modes
The ESP can be run in different operation modes. You can set and configure the mode by corresponding entries in the storm32web.cfg file, which is located in the data file folder, and which you just uploaded together with some other files in that folder. In the following, we will use the default configuration, which is the AP Bridge mode. The ESP provides then an access point, with these credentials:
- SSID = STorM32 ESP
- password = thisisgreat
- url = 192.168.4.1
- port = 80
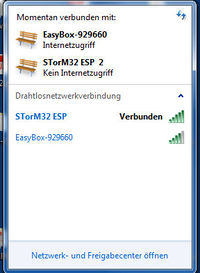
When powered up, you should find an entry 'STorM32 ESP' in the wlan list. For using it you will of course have to connect to it.
The AP Bridge mode allows us to access the STorM32 via both the GUI or the STorM32 Web App, but not both at the same time. Also, once the STorM32 Web App has been called, a connection to the GUI is not possible anymore (using first the GUI, and then the STorM32 Web App works fine, but not vice versa). In order to get access again via the GUI, you have to reset the STorM32 controller (or enter '192.168.4.1/bridge' in the browser).
Comment: This is so because for connecting with the GUI the ESP is switched internally to work as a bridge while for running the STorM32 Web App the ESP is switched internally to act as a web server. It is possible to switch from bridge to web server operation, but not back.
GUI
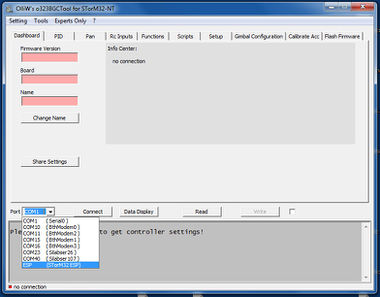
Using the Wifi connection with the GUI is trivial. When your wlan is connected to the access point 'STotrM32 ESP', then an entry 'ESP (STorM32 ESP)' should show up in the drop down list of the Port field. Select it, that's it. All GUI functions should work as normal.
Comment: It may happen that the connection will slightly hang at the first connection. This is because Windows has enumerated the access point, which lets the 'ESP (STorM32 ESP)' entry appear in the list, but is not yet ready, as also indicated by the mouse cursor.